Key Soft Skills Statistics (Editor’s Pick)
- 63% of employers and 70% of job seekers say finding the right talent or job is harder than last year due to AI and market changes.
- 90% of companies with more than 500 employees consider soft skills the most important factor when evaluating candidates.
- Over half of employers say identifying whether candidates have the right skills—especially soft skills—is the hardest part of hiring.
- Analytical thinking is the most in-demand soft skill, with 7 in 10 companies calling it essential.
- Soft skills appeared in 78% of global job postings, showing how widely employers now demand them.
- 63% of individuals who received soft skills training reported a positive impact on job performance.
- Poor communication costs large companies an average of $62.4 million per year, highlighting the financial impact of weak soft skills.
- The global soft skills training market reached $86.27 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $144.97 billion by 2035.
- 85% of employers use skills-based hiring, and 76% rely on skills tests, reflecting a shift away from credentials toward demonstrable skills.
- By 2030, 63% of all jobs will require soft skills, up from 53% in 2000, signaling strong future demand.

What if the skills most likely to decide your next hire, promotion, or career breakthrough aren’t the ones listed on your résumé?
In a job market reshaped by AI, automation, and constant change, what sets you apart is in how you think, communicate, adapt, and work with others.
If you’re an employer struggling to find people who truly fit, or a professional wondering how to stay relevant as roles evolve, soft skills are now the deciding factor behind hiring decisions, performance, retention, and long-term success.
Companies are investing billions into developing them, recruiters are prioritizing them over traditional credentials, and workers who master them are pulling ahead.
In this article, we break down over 40 powerful soft skills statistics that reveal what’s really happening in today’s workforce. These numbers show how they’re reshaping careers, redefining hiring, and determining who thrives in the future of work.
If you want to stay competitive, informed, and one step ahead, these are the stats you can’t afford to ignore.
General Soft Skills Statistics
Key Soft Skills Statistics & Facts (Editor’s Pick)
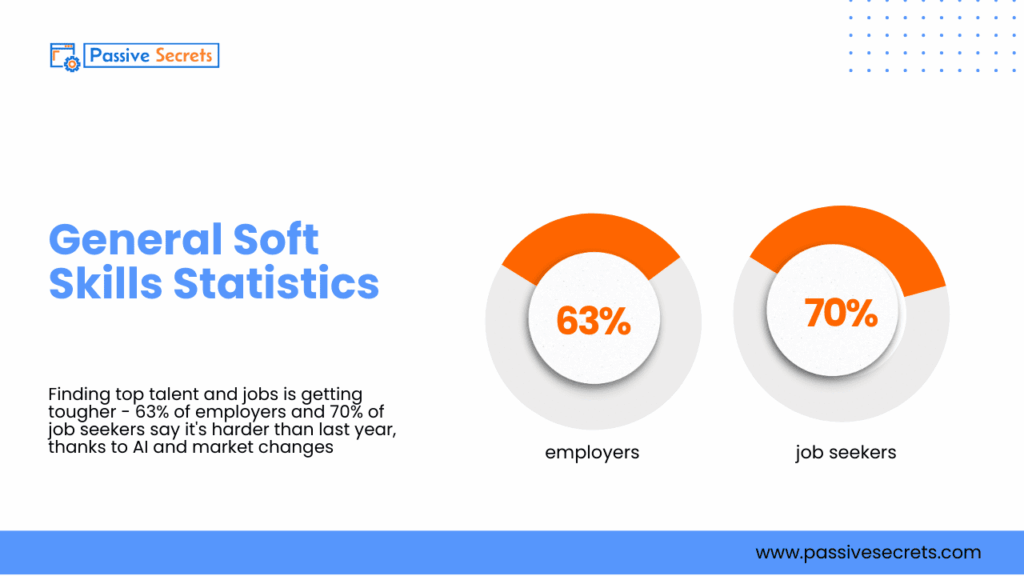
1. Finding top talent and jobs is getting tougher – 63% of employers and 70% of job seekers say it’s harder than last year, thanks to AI and market changes (source).
2. The importance of soft skills varied by education level: 95% of Doctorate holders,91% of Master’s and Bachelor’s degree holders valued them more than those with a high school diploma (74%) or a college degree (78%) (source).
3. Opinions varied across industries, withIT, finance, and education sectors seeing a much greater need for soft skills than travel and hospitality (source).
4. Female employees prioritized soft skills in the following order: communication (26.1%), problem-solving (21.5%), and time management (19.8%). In contrast, male employees ranked them as: problem-solving (21.5%), communication (21.2%), and critical thinking (19.8%) (source).
Why Soft Skills Matter Today
5. Over half of employers struggle to figure out if candidates have the right skills – soft or technical – it’s the toughest part of hiring now (source).
6. 80% of women acknowledged the importance of soft skills, while 90% of men viewed them as valuable in the workplace (source).
7. 84% of employees and managers think that new hires should have soft skills and show them during the hiring process (source).
8. Soft skills are seen as important because they can impact hiring decisions (22%), aid in career advancement (18%), and differentiate similar candidates (17%) (source).
9. The five industries that emphasize the importance of soft skills the most are: IT/Telecoms (99%), Finance (89%), Education (89%), HR (88%), and Healthcare (85%) (source).
10. 90% of companies with over 500 employees consider soft skills to be the most important factor (source).
11. Soft skills are deemed crucial for U.S employees because they can be a deciding factor in hiring (22%), are vital for professional growth (18%), and can set apart similarly qualified candidates (17%) (source).
Top Soft Skills in Demand
12. Analytical thinking is still the top skill employers want – 7 in 10 companies say it’s essential (source).
13. In Insurance and Pensions Management, curiosity and lifelong learning are huge – 83% say it’s a core skill, way above the 50% global average. Resilience, flexibility, and agility matter too – 94% say they’re crucial, vs 67% globally (source).
14. A 2024 survey found that 56% of security professionals considered communication skills, such as listening and speaking, to be the most important soft skills, while only 15% believed that honesty was a crucial trait for security professionals (source).
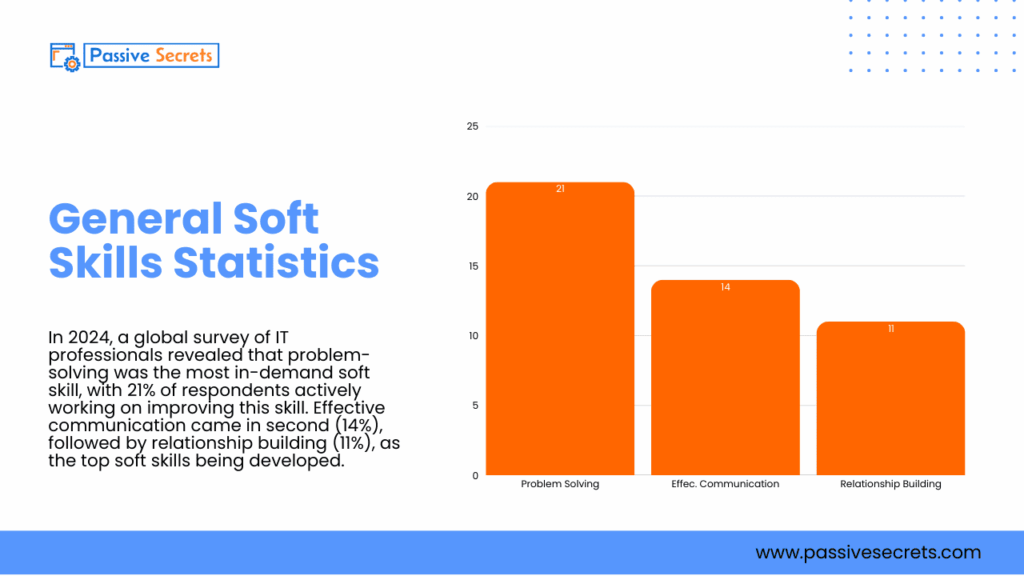
15. In 2024, a global survey of IT professionals revealed that problem-solving was the most in-demand soft skill, with 21% of respondents actively working on improving this skill. Effective communication came in second (14%), followed by relationship building (11%), as the top soft skills being developed (source).
16. In 2023, soft skills like communication, flexibility, and leadership were identified as the largest skill gaps among recent cybersecurity graduates (source).
17. About 90% of UK employers now consider soft skills crucial, with communication, leadership, and problem-solving emerging as the most sought-after skills in the UK job market (source).
18. In 2022, soft skills appeared in 78% of job postings worldwide in the past three months (source).
19. 45% of all LinkedIn Premium job postings in the past three months highlighted the importance of communication skills (source).
Impact of Soft Skills on Employment and Career Growth
20. 54% of workers used AI at work last year. Most are seeing benefits: about 3/4 say AI boosts productivity and work quality. Daily GenAI users are super optimistic: 9 in 10 say they’ve seen improvements and expect more gains (source).
21. Nearly 63% of individuals who underwent soft skills training reported a positive impact on their performance (source).
22. A survey of 400 large companies, each with 100,000 employees, revealed a staggering average annual loss of $62.4 million per company due to poor employee/management communication (source).
23. Organizations that prioritize soft skills in their workforce are likely to see a 26% increase in revenue growth, with 85% of job success attributed to these skills (source).
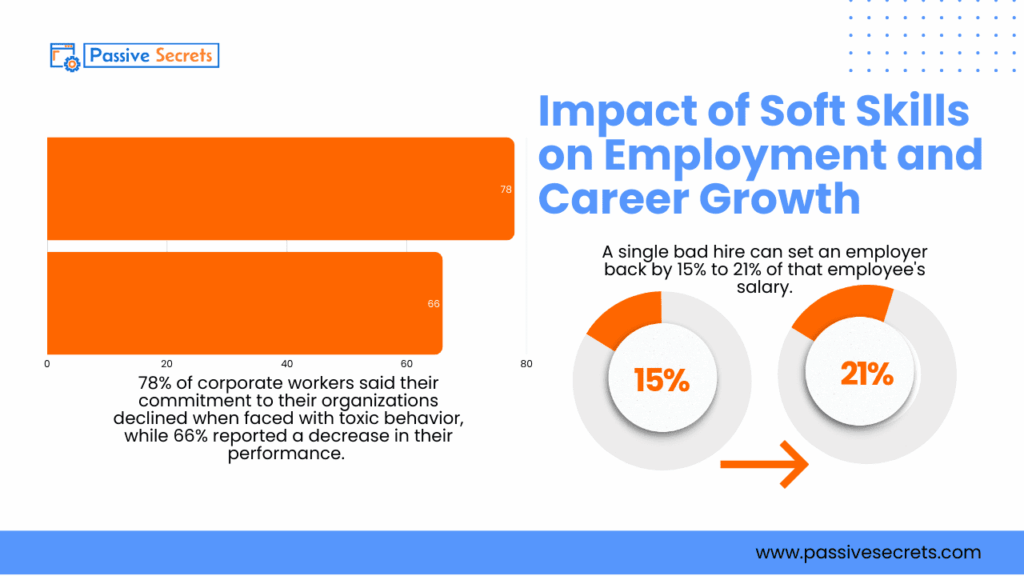
24. 78% of corporate workers said their commitment to their organizations declined when faced with toxic behavior, while 66% reported a decrease in their performance (source).
25. A single bad hire can set an employer back by 15% to 21% of that employee’s salary (source).
26. In retail, where turnover is high (60-70%), soft skill matching is key to reducing churn and boosting satisfaction (source).
Statistics on Soft Skill Training Investment
27. The Soft Skills Training Market was $86.27 billion in 2024. It’s expected to grow from $90.44 billion in 2025 to $144.97 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 4.83% (source).
28. The global soft skills training market was valued at $33.39 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach $92.59 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.40%. North America leads with over 32.9% share, driven by demand for leadership, communication, and adaptability skills (source).
29. The soft skills training market is projected to grow by USD 315.6 million, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 50.98% from 2023 to 2028 (source).
30. In a survey, employees received soft skills training via in-person (28%), virtual instructor-led (20%), virtual self-directed (20%), and hybrid (30%), with in-person training rated highest (source).
31. Companies that emphasize soft skills in their training and hiring processes benefit from a 30% higher employee retention rate and a 50% increase in employee engagement (source).
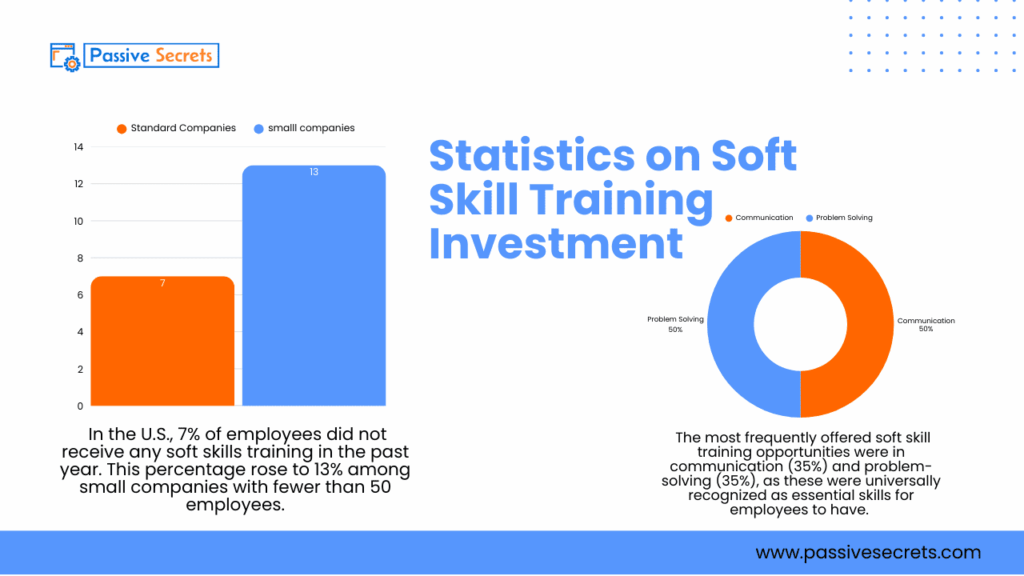
32. The most frequently offered soft skill training opportunities were in communication (35%) and problem-solving (35%), as these were universally recognized as essential skills for employees to have (source).
33. In the U.S., 7% of employees did not receive any soft skills training in the past year. This percentage rose to 13% among small companies with fewer than 50 employees (source).
34. Soft skills like communication, emotional intelligence, adaptability, and teamwork boost workplace culture and engagement. In-person training for these skills has a high satisfaction rate of 76% (source).
Soft Skills vs. Hard Skills: Employer Priorities
35. 85% of employers use skills-based hiring, up from 81% last year. 76% use skills tests to check candidates’ skills in 2025 – that’s the top method (source).
36. 85% of career success is attributed to strong interpersonal and soft skills, while hard skills, such as technical abilities and knowledge, account for only 15% (source).
37. Soft skills were the most sought-after qualities for 91% of management positions, 86% of business operations roles, and 81% of engineering jobs (source).
38. More than two-thirds (67%) of employers prioritize soft skills over educational qualifications when hiring, according to research by Indeed (source).
39. Although soft skills are rated more highly, over half (58%) of employers still consider A-level and BTEC results when screening candidates, with 53% acknowledging their importance beyond entry-level positions (source).
Future Projections for Soft Skills Demand
40. 71% of employees believe soft skills will be as important or more important in the future. In contrast, only 3% think AI will replace the need for soft skills in the workplace (source).
41. By 2030, nearly two-thirds of all jobs (63%) will require soft skills, a significant increase from 53% in 2000. This indicates a growing shift towards soft-skills-intensive occupations (source).
Trends In Soft Skills Acquisition Training
1. Reskilling and Upskilling
Reskilling and upskilling are key trends in soft skills development driven by rapid technological change.
Reskilling teaches employees new skills to transition into different roles as certain tasks become obsolete, focusing on adaptability, problem-solving, and teamwork.
Upskilling deepens employees’ expertise within their current roles, emphasizing advanced communication, leadership, and emotional intelligence.
Both approaches respond to the rising importance of soft skills, building a workforce that is technically proficient and agile in adapting to change.
2. Immersive learning through VRs and ARs
Immersive learning through Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) is a growing trend in soft skill training.
Virtual realities (VRs) create realistic scenarios for practicing soft skills, such as giving presentations or handling difficult conversations. These technologies help learners stay focused and motivated by providing interactive experiences for them.
Users get to receive immediate feedback on their performance, which also allows for immediate changes to be made. Additionally, VR and AR training can reach remote employees, making soft skills training more accessible to a wider range of staff.
These lasting experiences tend to leave more impact on employees and ensure memory retention compared to traditional training methods.
3. Peer-to-peer learning
Peer-to-peer learning is an important trend in soft skill training. It involves employees learning from each other rather than just from instructors.
This approach fosters collaboration and communication among team members.
Employees can share their experiences and insights, making the learning process more relatable and exciting.
This form of soft skill training also encourages active participation among employees and leads to better retention of skills. Peer feedback helps individuals identify strengths and areas that need improvement.
4. Data-driven learning approach
A data-driven learning approach is becoming a key trend in soft skill training. This method of soft skill acquisition training uses data to identify skill gaps and training needs within an organization.
The proper analysis of important performance metrics can help organizations tailor their training programs to address the specific needs of different employees and aid improvements.
This ensures that resources are used effectively and every training program is relevant to the employees involved. Data-driven insights also help measure the impact of training on performance, allowing for the continuous growth of an organization and effective soft skill development.
5. AI personalized learning
The increased use of artificial intelligence to create customized and personalized learning experiences for employees has been discovered to significantly influence soft skill training.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to analyze employees’ learning preferences and progress. This method uses artificial intelligence to tailor learning experiences to each employee’s unique needs.
This personalized approach helps employees engage more effectively with the training material and allows them to learn at their own pace. Additionally, AI can provide instant feedback and recommendations for further improvement.
Conclusion
Soft skills are crucial in corporate organizations, enhancing communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. Employers value these skills as they foster a productive and harmonious workplace.
Developing soft skills leads to success in jobs, better relationships, and improved overall well-being. By practicing soft skills, we can connect with others more effectively, achieve common goals, and make our personal and professional lives more efficient.
FAQs

Other Related Statistics You Should Know:
- 65+ Vital Leadership Statistics: Latest Trends and Insights
- 101 Billionaire Statistics: Surprising Insights About The World’s Wealthiest
- Business Loan Statistics: Trends Reshaping Funding for Millions of Small Businesses
- 70+ AI in Education Statistics That Prove the Future Is Already Here
- Women in Leadership Statistics: Insights into Global Gender Representation
- 95+ Fascinating Gift Industry Statistics to Surprise and Delight
- Top Business Coaching Statistics & Trends Every Leader Should Know
- How Much Are People Saving? Key Personal Savings Statistics Explained
- 40+ Useful Procrastination Statistics To Help You
- 90 Amazing Millionaire Statistics & Facts You Dare Not Miss
- 50+ Latest Life Coaching Statistics And Huge Trends
- 30+ Useful Real Estate Photography Statistics and Trends You Need to Know
- Data-Driven Decision-Making Statistics: Trends, Benefits & Challenges
- 54 Incredible Goal-Setting Statistics To Help You
- 80+ Franchise Statistics and Facts You Should Know
- 90+ Interesting Film Industry Statistics (NEW Report)
- The Ultimate Creator Economy Statistics Report: Trends, Tools, and Income
- 125+ Interesting Airbnb Statistics by Country (Deep Insights)
- The Most Important Wealth Management Statistics You Can’t Afford to Ignore
- 45+ Interesting Communication Skills Statistics & Huge Trends
- Body Language Statistics & Fun Facts To Boost Your Communication Skills
- 35 Interesting Public Speaking Fear Statistics & Fun Facts
- 25+ Most Interesting Emotional Intelligence Statistics & Fun Facts

