92% of employers and managers see workplace distractions as a major problem. From the constant ping of phone notifications to chatty coworkers, the modern work environment is rife with interruptions that impact productivity and focus.
To make matters worse, the human attention span steadily decreases yearly. Research shows that the average human attention span is shorter than that of a goldfish. This growing inability to focus hampers employee performance and costs businesses billions in lost productivity annually.
This article will explore the latest workplace distraction statistics, uncovering the key factors behind this decline and offering actionable insights to regain control over our attention.
Key Workplace Distractions Statistics & Facts (Editor’s Pick)
- Most US workers (79%) get distracted within an hour, and nearly 6 in 10 (59%) can’t focus for even 30 minutes without getting sidetracked.
- 92% of employers see lost focus as a major organizational problem.
- 60% of employees say they are more productive when they work remotely.
- 72% of workers say they turn off their cameras during a video meeting to hide what they are doing.
- Over 70% of US employees cite interruptions from colleagues as the top distraction preventing them from completing tasks.
- 92% of employees consider meetings to be “costly and unproductive.”
- Colleagues’ chatter (41%) is the top workplace distraction.
- The average worker checks their email 36 times an hour and takes 16 minutes to refocus after handling a new email.
- 36% of Millennials and Gen Z admit to spending two hours or more checking their smartphones at work.
- Meetings are among the most apparent examples of losing productivity.
- 15% of employees struggle with missed deadlines due to workplace distractions.
- Workplace distractions cost Australian workers 600 hours/year in lost productivity.
- Businesses across America lose upwards of $650 billion annually due to distracted employees during work hours.
- 43% of employers use software to curb digital distractions.
Defining Workplace Distractions
Workplace distractions are interruptions or disruptions that divert employees’ focus from their tasks or responsibilities, reducing productivity and efficiency.
These distractions can come from various sources, including technology, the work environment, personal issues, or interactions with colleagues. They are often cited as a significant barrier to achieving workplace goals and maintaining consistent performance.
Workplace distractions can either be internal (stress, anxiety, procrastination, or fatigue) or external (noise, interruptions from colleagues, technology).
General Workplace Distraction Statistics
1. Most US workers (79%) get distracted within an hour, and nearly 6 in 10 (59%) can’t focus for even 30 minutes without getting sidetracked. (source)
2. 67% of UK workers admit to getting distracted during the workday. Also, 15% of UK workers are distracted for 2 hours/day, and 7% for 3 hours/day (15 hours/week). (source)
3. Most people struggle to focus both at work (68%) and at home (62%). A significant portion (31%) can only concentrate for 10 minutes or less before getting distracted, and only 3 in 5 can maintain focus for 20 minutes or less. (source)
4. 92% of employers see lost focus as a major organizational problem. (source)
5. Over four-fifths (81%) of employees report being frequently distracted while working in the office. (source)
6. 99% of employees say they experience distractions while on the job. (source)
7. The average worker experiences 15 interruptions per hour worked, which means they are getting distracted every four minutes. (source)
8. Almost two in three employees say they struggle with productivity, time, and energy due to multiple meetings and email bloats. (source)
9. Over half (58%) of surveyed employees say they find it challenging to brainstorm in a virtual meeting. 57% say they find it difficult to follow a meeting if they arrive late. Another 55% say if the action items are unclear, they find it difficult to follow the meeting. (source)
10. Recently, Shopify revamped its meeting policies and banned unnecessarily long meetings. Hence, the company expects teams to increase productivity on completed projects by 25%. (source)
11. Between January and February, Shopify reduced the time spent on meetings by 33%. (source)
12. 40% of knowledge workers do not have a single opportunity to focus for a continuous 30-minute period during their workday. (source)
13. 60% of employees say they are more productive when they work remotely. (source)
14. 79% of employees feel distracted on a typical workday. (source)
15. 75% of employees believe that working remotely reduces distractions. (source)
16. Prime time for distraction hits at midday, with 46% answering that noon to 3 pm is their most distracted period. (source)
17. A recent study conducted by Poly found that 99% of employees say they are distracted from their tasks sometime during their workday. (source)
18. It takes an average of 23 minutes and 15 seconds to get back to the task after being distracted. (source)
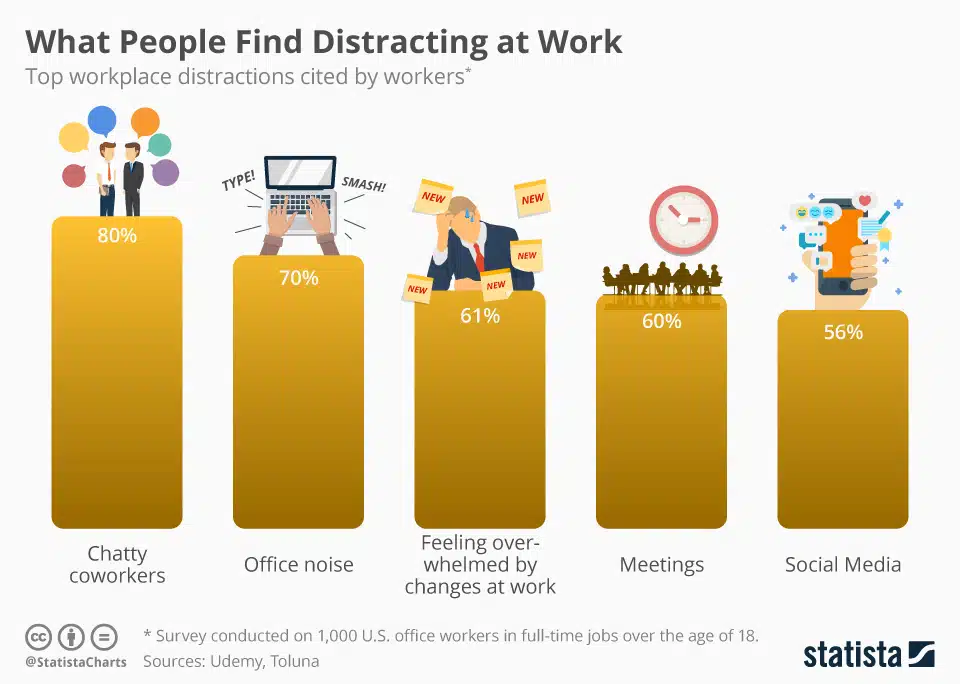
19. Udemy and Toluna report that 80% of people report being distracted by chatty coworkers, the number one office place distraction. (source)
20. The University of California, Irvine, found that 50% of our distractions are self-induced. This means that we can stay away and not surrender ourselves to the temptations of checking our cell phones or emails, but we choose not to. (source)
21. Gen-Z and Millennials are the most distracted at work. 84% of Gen-Z and Millennial workers say they are easily distracted on video calls or meetings. (source)
22. 72% of workers say they turn off their cameras during a video meeting to hide what they are doing. (source)
23. 78% of workers believe in-person meeting etiquette has worsened since the Covid pandemic. (source)
The Most Common Workplace Distractions
24. According to a recent Microsoft survey, the number 1 workplace distraction is inefficient meetings. (source)
These meetings affect productivity and cause employees stress. An inefficient meeting is a meeting that causes unnecessary stress to the employees. They don’t have a clear purpose and are often long.
25. Over 70% of US employees cite interruptions from colleagues as the top distraction preventing them from completing tasks. 62% say phone notifications are their major distractions. (source)
26. 92% of employees consider meetings to be “costly and unproductive.” (source)
27. Office workers are more focused than remote workers, with 33% distracted for 30 minutes or less. Remote workers’ top distraction is their phone (27%), while office workers are most distracted by colleagues’ conversations (38%). (source)
28. Colleagues’ chatter (41%) is the top workplace distraction, but nearly 2 in 5 (37%) admit to distracting themselves by socializing with others while working. (source)
29. Most UK employees (77%) find workplace digital tool notifications distracting, with 31% experiencing distractions every 15 minutes, resulting in approximately 160 weekly distractions. (source)
30. 45% of employees say workplace digital notifications are irrelevant to their jobs. (source)
31. Employees admit to checking their devices for personal reasons frequently, with 42% doing so up to 5 times a day and 37% doing so 5-10 times a day, highlighting a significant distraction at work. (source)
32. 71% of employees blame their coworkers as the primary source of distraction, causing them to lose focus and struggle to concentrate on their work. (source)
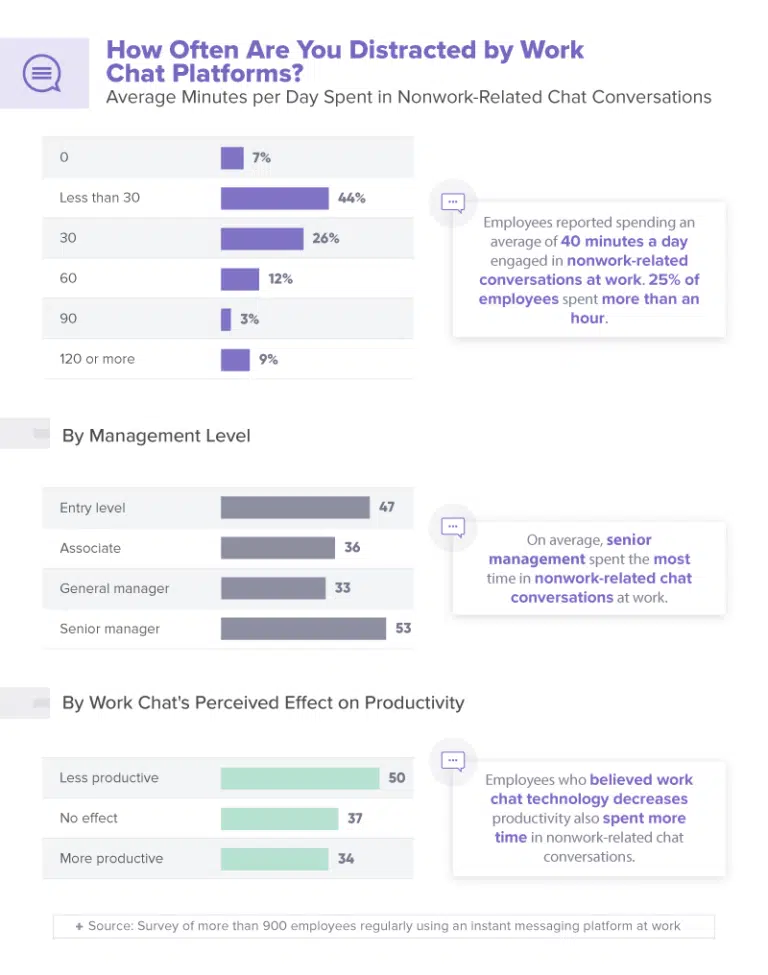
33. Employees spend an average of 40 minutes daily in nonwork-related chat conversations at the workplace. (source)
34. 76% of employees consider coworker interruptions, including noise and gossip, as major distractions. (source)
35. 30% of employees are distracted by the internet. (source)
36. 26% of U.S. workers say distractions from world events make it difficult to care about their jobs. (source)
37. The average worker checks their email 36 times an hour and takes 16 minutes to refocus after handling a new email. (source)
38. Employees attend about 62 meetings per month, in which 91% of workers say they daydream. And it takes most employees two hours per day to recover from interruptions from co-workers. (source)
39. 26% find the sound of coffee being made to be a moderate to very high distraction, while 46% are distracted by pets in the office. (source)
However, visiting children causes moderate to very high distractions for 53% of people.
40. Employees spend about 32% of their workdays on Facebook. (source)
41. 36% of Millennials and Gen Z admit to spending two hours or more checking their smartphones at work. (source)
42. 66% of employees with work chat apps on their phones are distracted for an additional 16 minutes daily by nonwork-related conversations, totaling 43 minutes. (source)
43. Employees are spending an enormous amount of time (2.5 hours) during each workday accessing digital content that is unrelated to their jobs. (source)
44. Of all the office distractions, meetings are among the most apparent examples of losing productivity. (source)
45. Office noise is the second most cited workplace disturbance, with seven out of ten respondents citing noise as a top bother in their day-to-day workflow. (source)
46. Specifically, 51% of workers stated that it was harder for them to conduct phone calls, and 93% said office distractions made it hard to conduct video calls. (source)
47. 48% of employees said that office distractions made focusing difficult. (source)
48. Meetings (60%) and social media (56%) complete the spots of job distractors with positions four and five. (source)
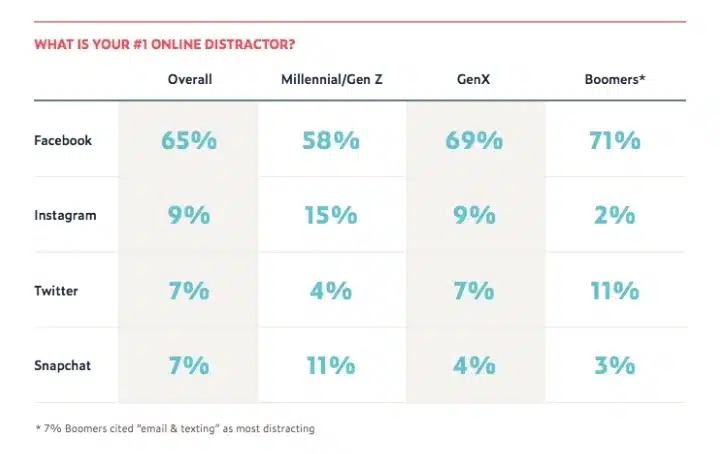
49. Employees were asked to rate social media sites and communication tools in terms of their distraction prowess. Facebook came in first (65%), followed distantly by Instagram (9%), Snapchat (7%), and Twitter (7%). (source)
50. 60% of people view meetings as distractions interrupting their work and preventing them from completing tasks. (source)
51. Millennials and Gen Z are also the most likely age group to describe themselves as distracted at work. (source)
52. Over a third of millennials and Gen Z (36%) spend two hours or more checking their smartphones at work. That adds up to at least 10 hours weekly when they do something outside their responsibilities. (source)
53. Among millennials and Gen Z, 74% admit to being distracted, with 46% feeling unmotivated and 41% experiencing stress. (source)
54. A massive 40 million Americans deal with anxiety in the workplace almost every day, and many things can trigger it. (source)
55. Only 24% of employees report never checking email after hours. That leaves a whopping 76% of employees checking work emails after hours. (source)
56. 7 out of 10 employees say that emails have a detrimental effect on their work quality. (source)
57. 76% of U.S. employees say they get more distracted on video calls than in-person meetings. (source)
Impact Of Workplace Distraction On Productivity
58. Managers see lack of focus (64%) and motivation (49%) as top issues with Gen Z workers. (source)
59. Most employees (60.6%) rarely or never have a 1-2 hour block of uninterrupted, focused work daily. Additionally, 72.5% admit to being present in meetings but not fully engaged or paying attention. (source)
60. The Udemy study found that 84% of employees believe they can refocus on their tasks within 30 minutes of an interruption. Additionally, 60% of baby boomers believe they can refocus on their tasks in less than five minutes. (source)
61. 15% of employees struggle with missed deadlines due to workplace distractions. (source)
62. 48% of workers believe that office distraction prevents them from focusing effectively on their job. (source)
63. When distracted at work, 51% find it harder to manage phone calls, and 93% say office distraction makes managing video calls more challenging. (source)
64. A researcher summarized an info-tech research that US companies lose as much as $588 billion yearly due to lost productivity. (source)
65. Employees are productive for less than 60% of their time in the office or at remote work simply because of distractions. (source)
66. Employees report that frequent distractions compromise the quality of their work. (source)
The Cost Of Workplace Distraction
67. Employers estimate that distractions cost them significant time, with 1/3 saying 5 hours/week are lost, and another 1/3 estimating 6-10 hours/week (up to 25% of the workweek) in lost productivity. (source)
68. Think Tank ascertained from figures that when added together, interruptions cost companies globally around €58 billion per year. (source)
69. UK workers lose up to 15 hours/week (74 days/year) due to distractions. (source)
70. Workplace distractions cost Australian workers 600 hours/year in lost productivity. (source)
71. Almost 36% of employers say one to five hours are lost each week per employee, while 34% say six to ten hours are lost per employee. In other words, up to a quarter of the typical 40-hour work week. (source)
72. 15% to 24% more time is added to the task for every single interruption, depending on the complexity. Taking it at 15%, that’s an average of three full working days a month lost purely to interruptions. (source)
73. The average worker wastes 60 hours monthly due to workplace distractions. The distractions can come from various sources, including colleagues, phone notifications, and meetings. Workplace distractions can lead to reduced productivity, increased stress, and even financial losses. (source)
74. Interruptions cause employees to take 27% more time to complete a task, commit up to 2x as many errors, and experience 2x the anxiety. (source)
75. Businesses across America lose upwards of $650 billion annually due to distracted employees during work hours. (source)
76. Statistics reveal that in the US, about $25 million of wastage happens daily because fruitful working time is spent in unnecessary meetings. (source)
Solutions To Minimize Workplace Distractions
77. Music improves concentration for 80% of UK employees, and 63% say its impact varies depending on the task at hand. (source)
78. 43% of employers use software to curb digital distractions. (source)
79. Almost 78% of employees agree that flexibility at the workplace enables them to be more productive. (source)
80. 50% of employees can work more efficiently when telecommuting with diminished stress levels. (source)
81. Employers use productivity software (53%) and internal systems (56%) to manage workloads and assignments. (source)
FAQs on Workplace Distraction Statistics

Other Workplace Statistics Articles You Should Know:
- 80+ Employee Benefit Statistics: Insights and Trends
- The Most Important Wealth Management Statistics You Can’t Afford to Ignore
- Enterprise Data Management: Essential Statistics and Emerging Trends
- 93 Talent Management Statistics to Help You
- Top Reputation Management Statistics and Trends to Improve Your Brand
- 36 Helpful Social Worker Burnout Statistics To Know
- 100 Business Process Outsourcing Statistics & Facts
- Top HR Outsourcing Statistics and Trends Every Business Must Know
- The Top Outsourcing Statistics You Shouldn’t Ignore
- 47+ Shocking 4-day Work Week Statistics To Know
- 105+ Supply Chain Statistics & Facts You Can’t Ignore
- 50+ Interesting Employer Branding Statistics And Trends
- Job Seekers Statistics: Unemployment Rates, Preferences, Challenges
- 95 Interesting Job Interview Statistics and Huge Trends To Know
- 60+ Helpful Change Management Statistics & Facts
- 65+ Employee Performance Management Statistics & Trends
- Workforce Management Statistics: Trends, Insights, & Opportunities
- Workplace Romance Statistics: How Common Is Workplace Romance?
- 40+ Top Workplace Conflict Statistics You Should Know
- The State of Workplace Communication: Key Statistics and Trends
- 55 Workplace Collaboration & Teamwork Statistics