
Attracting and keeping top talent has never been more challenging or more critical for organizations. Talent drives innovation, growth, and success, yet managing, retaining, and developing the right people is becoming increasingly complex. From AI transforming recruitment to the growing focus on upskilling and employee engagement, HR leaders are navigating a rapidly evolving landscape.
But hiring is just the beginning. Once employees are on board, keeping them motivated and engaged is essential.
However, engagement levels often fall far short of expectations, leaving organizations struggling to unlock their workforce’s full potential.
In this article, we dive into key talent management statistics for 2025, from market growth and software adoption to talent acquisition trends and employee development insights. These numbers reveal what’s really happening in the world of work and provide actionable insights to help your organization attract, retain, and grow the talent it needs to thrive in today’s competitive business environment.
Top Talent Management Statistics (Editor’s Picks)
- 51% of organizations hired a more diverse workforce; 45% expanded recruitment geographically.
- 71% report that hybrid/remote work improves the ability to attract and retain employees.
- 81% of organizations enhanced their employer brand to attract and retain talent.
- 18% of HR professionals prioritize certifications/non-degree credentials; 53% still prioritize college degrees.
- 66–69% of organizations advertise flexible roles; hybrid policies improve productivity by 45% and engagement by 35%.
- 78% of HR professionals report feeling engaged and energized at work.
- 67% of employees would remain with their company if offered upskilling and career advancement opportunities.
- Only 15% of frontline managers and employees feel connected to their purpose on the job.
- Around 50% of workers feel exhausted or burned out, highlighting the need for mental health support.
- 91% of organizations view technical training as an effective strategy for retaining employees.
- 84% provide leadership training; 80% offer online learning platforms and resources.
- 91% of L&D professionals see continuous learning as vital; 88% cite learning opportunities as the top retention strategy.
- 54% of organizations design job roles to highlight specific skills; 46% develop skills internally.
- 46% of organizations offer apprenticeships; ~33% provide graduate/entry routes; ~25% run intern schemes.
- 69% of HR professionals report that competition for highly qualified talent has intensified; 56% note retention challenges.
- 67% of organizations cite talent scarcity as a major barrier to growth.
- 60% report it is harder to retain talent than the previous year; 37% have initiated retention improvements.
- 30% of workers cite non-competitive salaries as the primary barrier to attracting top talent.
- 24% of organizations reduced focus on diversity, equity, and inclusion in tech hiring; 39% said the decision came from leadership.
- 63% of organizations believe greater reliance on data will be key to HR success in the future.
Talent Management Market Size
1. In 2025, the talent management market was valued at USD 12.85 billion and is forecasted to grow to USD 26.40 billion by 2030, reflecting a CAGR of 15.48%. North America generated 38.50% of total revenue in 2024, while Asia-Pacific is advancing rapidly with an 18.90% CAGR, driven by extensive digital transformation initiatives across India, China, and Southeast Asia.
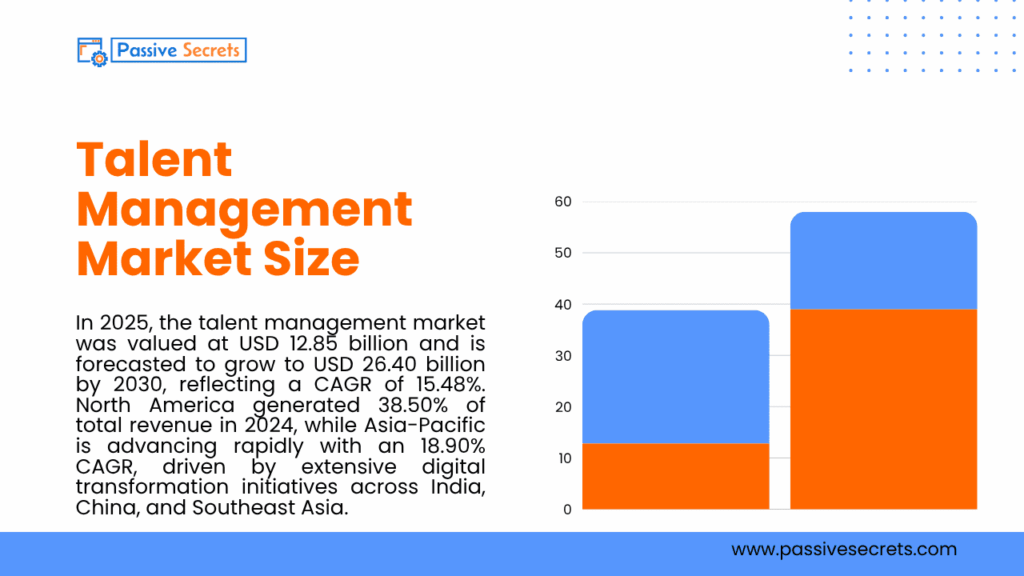
Learning & Training Management represented the largest market share in 2024 at 28.30%. In contrast, Generative-AI Talent Analytics is the fastest-expanding segment, with a CAGR of 24.80%, signaling a move away from static HR reporting toward predictive workforce intelligence. (source)
2. The HR technology market in India reached US$1,040 million in 2023 and is projected to reach US$2,170 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 8.3% from 2024 to 2032. (source)
3. Johnson & Johnson achieved a 20% increase in voluntary learning after implementing AI-driven skills inference, which analyzes work patterns and project results to create dynamic employee profiles. This approach helped address identification gaps that had left 87% of executives unsure about the actual shortcomings of their workforce. (source)
4. The global celebrity talent management market was valued at USD 15,905.84 million in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 25,931.83 million by 2031, with a CAGR of 5.58% from 2022 to 2031. (source)
5. The North American Talent Management Software Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.6% from 2023 to 2030. (source)
Talent Management Software Statistics
6. The global market for talent management software was valued at USD 10.09 billion in 2024. It is expected to expand from USD 11.30 billion in 2025 to USD 25.01 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.0% over the forecast period. In addition, the U.S. talent management software market is anticipated to experience substantial growth, with its value projected to reach approximately USD 5,180.4 million by 2032. (source)
7. By 2025, the proportion of HR leaders leveraging AI tools increased to 38%, up from 19% in 2023. Analysts estimate that AI could unlock as much as 67% in value potential across recruitment, performance management, and people analytics functions. (source)
8. The Talent as a Service market is projected to be worth USD 593.3 million in 2025 and is expected to expand to USD 1,793.9 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 11.7% over the forecast timeline. (source)
9. Regarding AI adoption, most HR and talent acquisition professionals report using or planning to use advanced tools for candidate matching and ranking (61%), with growing interest also in generative AI (56%), AI chatbots (48%), and AI-powered resume parsing (45%). (source)
10. Over two-thirds (67%) of talent professionals surveyed see rising AI adoption as the leading talent trend for 2025, with 53% pointing to data analytics as the next most significant. (source)
11. Employers’ top three planned innovations in talent acquisition for next year are: leveraging AI to improve candidate search and screening (27%), expanding the use of people analytics in hiring (26%), and adopting automation tools to manage candidate relationships (21%). (source)
12. In organizations leveraging AI, 94% of HR professionals report that candidates with AI expertise demand higher salaries compared to other tech roles. Nearly 68% of employers meet these requests, with larger U.S. companies more willing to pay a premium. In fact, 78% of U.S. firms with 2,500+ employees typically agree to higher salaries, compared with 64% of smaller organizations. (source)
13. Among companies using AI, 99% of HR professionals reported a rise in requests to include AI skills in job requirements for roles not specifically focused on AI—up from 96% the year before. Additionally, over one-third (35%) of U.S. hiring managers observed a notable increase. (source)
14. Nearly 94% of organizations anticipate AI will generate substantial value in core operations, heightening demand for skilled talent. In fact, organizations are 2.7 times more likely to have expanded their workforce than reduced it because of AI, resulting in a net hiring impact of +21% and further straining the talent supply. (source)
15. The increasing adoption of cloud-based platforms and mobile-based personnel management systems is a key driver of growth in the talent management software market. (source)
16. The European Talent Management Software Market is expected to grow at an 11% CAGR from 2023 to 2030. (source)
Talent Acquisition Statistics
17. Among organizations that sought to fill vacancies, 51% reported hiring a more diverse workforce than the year before, while 45% expanded recruitment across a broader geographic area within the UK. (source)
18. Providing hybrid or remote work options can broaden the talent pool, with 71% of organizations offering such arrangements reporting that it has improved their ability to attract and retain employees. (source)
19. In the UK, 10% of organizations plan to scale back recruitment of migrant workers, while 23% intend to prioritize developing internal skills and 18% aim to enhance job offerings to better attract UK-born talent. (source)
20. Overall, 47% of organizations handle all recruitment internally through direct hiring, a practice most prevalent in non-profits (77%) and least common in the private sector (43%). (source)
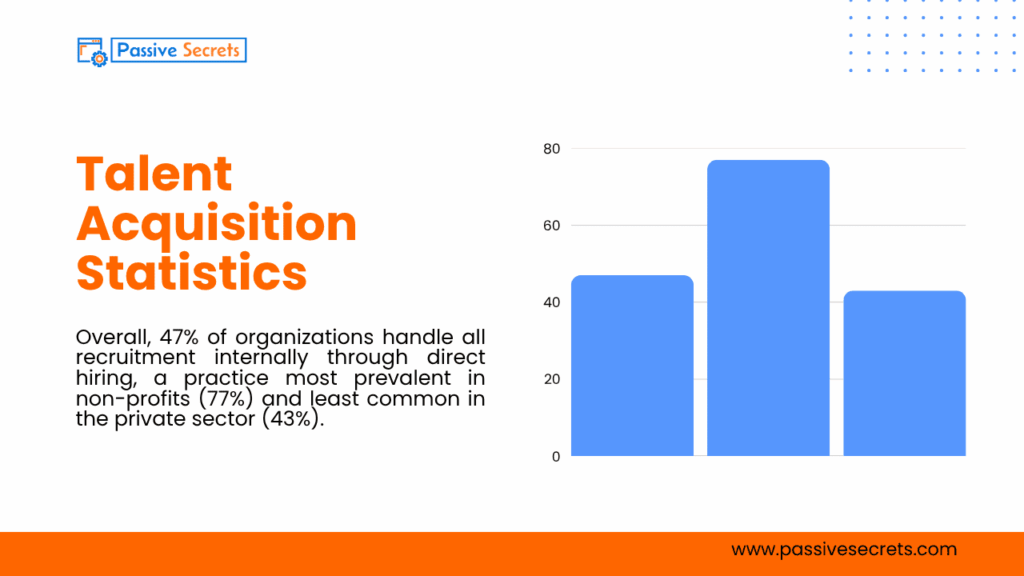
21. About 20% of organizations manage recruitment internally while also working with agencies, and 31% adopt a mixed approach combining in-house and outsourced methods. Only 3% fully outsource their recruitment processes. (source)
22. A strong employer brand is essential for attracting and retaining talent, with 81% of organizations reporting they took steps to enhance their brand in the past year. (source)
23. The majority of organizations now provide some form of hybrid or remote work, with 29% noting an increase in such arrangements over the past year. Similarly, 54% now advertise at least some roles as “location flexible.” (source)
24. Around 76% of organizations have either implemented or are planning to implement a skills-based approach, with the greatest advancements seen in talent acquisition. (source)
25. When examining the key obstacles to internal mobility, HR and talent acquisition professionals most frequently pointed to challenges in identifying and aligning skills with available roles (51%). Other barriers included limited technology or tools to support mobility (30%) and poor communication of internal mobility policies and opportunities (26%). (source)
26. While 45% of respondents rank acquiring top talent as a key priority, a majority (58%) rate their talent attraction strategies as only “somewhat effective,” pointing to considerable room for improvement. (source)
27. Of the organizations that have embraced a skills-based approach, most (80%) have implemented it in talent acquisition, while 69% have applied it to training and development, and 46% to internal mobility. (source)
28. Four in ten (40%) talent specialists expressed concern that excessive reliance on AI in recruitment could make the process feel impersonal and lead to losing strong candidates. (source)
29. About 63% of hiring leaders report that finding candidates with sufficient AI skills is harder than sourcing talent for other tech roles. The challenge is particularly acute in the U.S., where nearly 18% of hiring professionals say it is “significantly more difficult,” compared to just 9% in the UK. (source)
30. Three-quarters (75%) of respondents say their companies are hiring AI talent without investing in sustainable pipelines of qualified, high-potential candidates. This issue is even more pronounced at organizations that are reducing or cutting DEI initiatives, where the share rises to 84%. (source)
31. Currently, 18% of HR professionals say they are more likely to consider certifications and non-degree credentials first when hiring for positions in remote software engineering, data analytics, data science, and UX design. This share has tripled over the last two years. In comparison, slightly more than half (53%) still prioritize a candidate’s college degree. (source)
32. Around 71% of organizations regard certifications as a key factor in hiring, seeing them as proof of a candidate’s professional capabilities. (source)
33. A shortage of skilled workers ranks among the top three barriers to adopting new technologies, mentioned by 44% of respondents, behind budget limitations (52%) and security or privacy concerns (45%). (source)
34. The talent acquisition segment held the largest share in the talent management software market in 2023 and is expected to continue growing due to the demand for efficient onboarding, recruiting, and sourcing processes. (source)
35. Organizations increasingly offer better pay and benefits to address recruitment
difficulties (36%, up from 29% last year). (source)
36. Pay and benefits have emerged as one of the top factors in employer branding to attract candidates. However, nearly 60% of organizations do not consider them among their primary attractors. (source)
37. Flexible working options are advertised for at least some jobs by 69% of organizations. It’s increasingly viewed as an effective method for attracting candidates, with 54% of those facing recruitment challenges opting to offer greater work flexibility. (source)
38. 66% of organizations have implemented hybrid/remote working policies, and 47% advertise jobs as ‘open to location.’ Such flexibility has helped 68% of these organizations attract and retain talent while also boosting productivity by 45% and engagement by 35%. (source)
39. Formal diversity policies are in place at 61% of organizations, although efforts to attract diverse candidates could be more proactive and comprehensive. One-third of organizations have achieved a more diverse workforce than the previous year. (source)
Employee Engagement Statistics
40. Around 70% of individuals derive their sense of purpose from their work, underscoring the importance of aligning daily tasks with meaningful outcomes. (source)
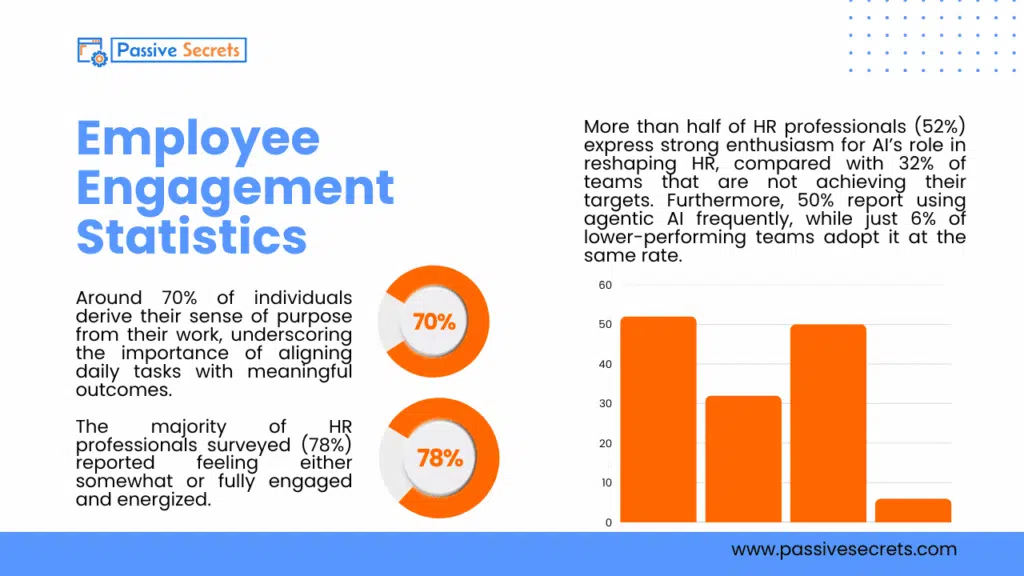
41. The majority of HR professionals surveyed (78%) reported feeling either somewhat or fully engaged and energized. (source)
42. More than half of HR professionals (52%) express strong enthusiasm for AI’s role in reshaping HR, compared with 32% of teams that are not achieving their targets. Furthermore, 50% report using agentic AI frequently, while just 6% of lower-performing teams adopt it at the same rate. (source)
43. Nearly 46% of millennial HR professionals report facing emotional strain from handling employee issues, a higher share than any other generation. (source)
44. About 67% of employees say they would remain with their company if given upskilling and career advancement opportunities—even if they dislike their current job. (source)
45. Organizations are 3.2 times more likely to prioritize upskilling their current workforce over external hiring, reflecting a focus on unlocking the untapped potential of existing talent. (source)
46. Only 15% of frontline managers and employees report feeling connected to their purpose while on the job. (source)
47. About half of workers feel exhausted (51%), drained (45%), or burned out (44%) due to their job, with stress, overwhelm, and anxiety being common experiences, emphasizing the need for organizations to prioritize mental health support. (source)
Talent Development and Upskilling Statistics
48. According to 43% of HR professionals, employees are increasingly being asked to assume extra duties and responsibilities without a corresponding salary increase — a practice often referred to as a “dry promotion.” (source)
49. To address talent needs, 56% of organizations are focusing on developing internal talent, while 35% have turned to technology and automation to replace certain roles over the past year. (source)
50. Two-thirds (66%) of HR professionals report that their organization has a formal EDI strategy, though 8% are unsure. Such strategies are most prevalent in the public sector (85%), followed by non-profits (72%) and private organizations (62%), and are more common in larger organizations across all sectors. (source)
51. For organizations that have implemented a skills-based approach, the leading strategies to ensure their workforce has the right capabilities include designing job roles and descriptions that highlight specific skills (54%) and developing skills internally (46%). (source)
52. A large majority of respondents (84%) said their organizations provide leadership training—an essential step in today’s environment where resilience and adaptability are crucial. In addition, 80% reported offering access to online learning platforms and resources, reflecting a strong focus on continuous skill development. (source)
53. A vast majority of organizations (91%) view technical training as an effective strategy for retaining employees and reducing sunk costs. (source)
54. About 84% of organizations see open-source culture as a powerful tool for retaining talent, giving employees both a technical edge and unique career development opportunities in a highly competitive market. (source)
55. In 2024, employees averaged 13.7 hours of formal learning each, a decrease from 17.4 hours in 2023, continuing a steady decline observed since 2020. (source)
56. Nearly half (49%) of learning and talent development professionals report a skills crisis, agreeing that their executives worry employees lack the capabilities needed to carry out the business strategy. (source)
57. 91% of L&D professionals see continuous learning as increasingly vital for career growth. Similarly, 88% of organizations are concerned about employee retention, with providing learning opportunities cited as the most important strategy to retain talent. (source)
58. Career development champions are 32% more likely than non-champions to implement AI training programs this year and 88% more likely to provide career-advancing gig opportunities or project-based learning. (source)
59. Nearly 40% of organizations focus more on developing internal talent to meet their needs, while 26% have replaced some jobs with technology and automation in the past year. (source)
60. Nearly 38% of organizations are ramping up efforts to address talent needs by nurturing internal talent. Upskilling existing employees is the predominant strategy to combat recruitment difficulties, chosen by 60% of companies. (source)
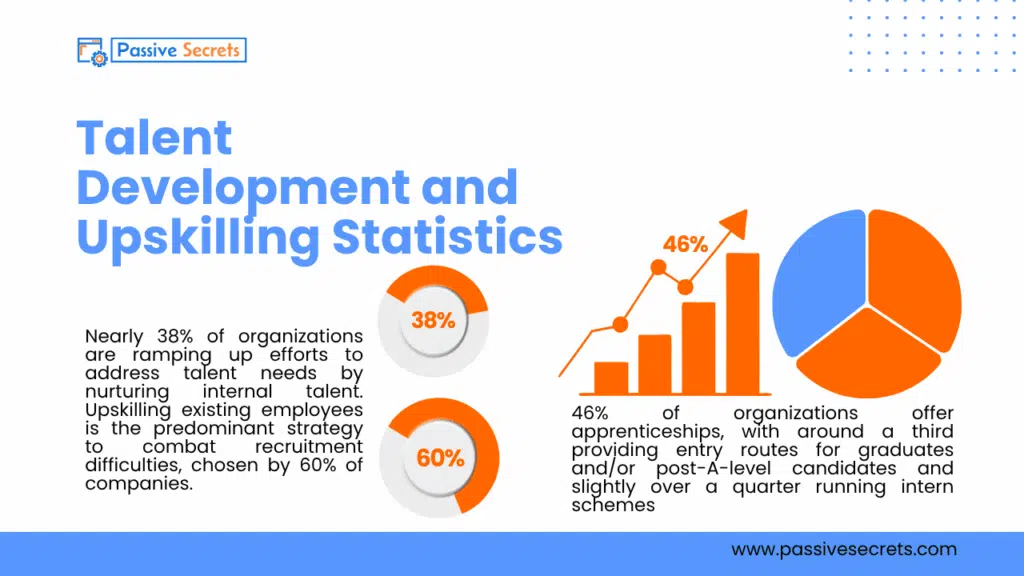
61. 46% of organizations offer apprenticeships, with around a third providing entry routes for graduates and/or post-A-level candidates and slightly over a quarter running intern schemes. (source)
Talent Management Challenges
62. Notably, 69% of HR and People professionals say competition for highly qualified talent has intensified over the past year, and 56% report greater challenges in retaining employees. (source)
63. Just over half of organizations (53%) see aligning workforce capabilities with business objectives as the main goal of workforce planning, yet 52% cite accurately forecasting workforce needs as their biggest challenge—highlighting obstacles to achieving significant progress in this area. (source)
64. About 24% of HR professionals surveyed reported that their companies have reduced or dropped their focus on diversity, equity, and inclusion in tech hiring over the past year. Of those organizations, 39% said the decision came from board or company leadership. (source)
65. The vast majority of organizations (89%) report that expanding the scope of an existing role is a key factor when evaluating potential. (source)
66. Just 36% of organizations qualify as career development champions, with strong programs that drive business outcomes. Another 31% have programs in place but with limited uptake, while 33% either lack initiatives altogether or are only in the early stages. (source)
67. When identifying the top three obstacles to career development, respondents highlighted time and resource constraints as key issues: 50% report that managers lack adequate support, 45% say employees are unsupported, and 33% point to insufficient support within talent teams themselves. (source)
68. In a survey, 76% of advertisers, agencies, publishers, platforms, and ad tech companies said inadequate training and development was a key reason for talent scarcity, and the same percentage cited insufficient prioritization of talent management. (source)
69. In 2023, the biggest challenge for Global Business Services organizations worldwide was career progression and opportunities, with nearly half of respondents highlighting this issue. (source)
70. In a global survey, 48% of advertisers, agencies, publishers, platforms, and ad tech companies believed the industry was facing its worst-ever talent crisis, while 21% disagreed. (source)
71. 67% of respondents in a survey said talent scarcity was a major barrier to growth. (source)
72. 60% of APAC’s advertisers, publishers, platforms, and ad tech companies believed the advertising media industry faced its worst talent crisis. This figure was just over 50% in the U.S. and 44% in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. (source)
73. In the same survey, around 75% of respondents acknowledged some talent scarcity, with 85% of ad agencies reporting this issue. (source)
74. One-third (33%) of people managers feel their role isn’t worth the stress, and 40% experienced a decline in mental health after taking on a leadership position. (source)
75. Only 13% of HR leaders consider their talent management practices excellent, while 70% rate their organization’s ability to meet talent needs as mediocre. (source)
76. Talent management has been a key priority for only 38% of organizations over the past year, an increase from 30% in 2021, albeit lower than in previous years. (source)
77. Overall, 81% of organizations attempted to fill vacancies, and 77% encountered challenges attracting candidates, up from 49% in 2021. (source)
78. Recruiting for senior and skilled roles posed the greatest difficulty at 58%, while 26% struggled with hiring low-skilled candidates. (source)
79. 60% reported it is now harder to retain talent than the previous year, prompting 37% to initiate retention improvement efforts, up from 29% in 2021. (source)
80. 80% of UK employers face challenges finding talent with the necessary skills, marking a 17-year high. (source)
81. Globally, 4 out of 5 employers find it difficult to secure needed talent in 2023, up 2 percentage points from the previous year. And substantially higher than the 2015 figure of 14%. (source)
82. Demographic shifts have worsened talent scarcity, including declining birth rates and increased early retirements. (source)
83. UK employers report talent shortages three percentage points higher than the global average of 77%. (source)
84. 70% of respondents acknowledge heightened competition for skilled talent over the past year, with 60% indicating increased difficulty in talent retention compared to a year ago. (source)
85. An Australian study of 500 employers and 1,000 workers shows that 89% of employers and 71% of employees doubt their company’s ability to recruit skilled personnel this year. (source)
86. The primary issue hindering employers from attracting top talent is non-competitive salaries, identified by 30% of workers. (source)
87. Limited career advancement opportunities are a significant concern, with 30% of employers and 26% of workers worrying about this. (source)
88. Financial and accounting professionals are the most anxious about retention policies (74%), followed by business support (73%) and technology sector employees (67%). (source)
89. One in four executives (24%) believes meeting this year’s business demand will be challenging with the current talent model. (source)
90. Despite 58% seeing AI as delivering over 30% productivity gains, two-thirds are wary of implementing new technology without transforming work processes. (source)
91. Less than 30% of HR leaders in Australia view AI as a tool to enhance human intelligence, missing opportunities beyond automation. Only 16% of employees report job redesigns benefiting from new technologies. (source)
92. In Australia, 62% of businesses struggle to find talent, exceeding the global average of 50%. Additionally, 46% have difficulty retaining employees, higher than the global average of 40%. (source)
The Future of Talent Management
93. About 63% of organizations believe that greater reliance on data will be key to the future success of HR, supporting its continued shift toward a more strategic and advisory role. (source)
94. The human capital management solutions market is expected to grow by USD 16.23 billion between 2024 and 2029, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.1% over the forecast period. (source)
95. A new report by KBV Research projects the Global Talent Management Software Market will reach $19.4 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 11.4% during the forecast period. (source)
96. The Performance Management segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12% from 2023 to 2030. (source)
97. The On-premise segment led the Global Talent Management Software Market by Deployment in 2022, expected to reach a market value of $10.0 billion by 2030. (source)
98. Around 40% of companies expect to boost their recruitment and talent management budgets in the coming year. A significant rise compared to previous years reflects growing challenges and resourcing expenses. (source)
99. Artificial intelligence (AI) is beginning to transform workplaces globally, with 30% of workers worldwide and 41% in the Asia Pacific region utilizing AI in daily tasks. (source)
Talent Analytics and Metrics
100. About 66% of organizational leaders identified talent assessment as the greatest benefit, emphasizing its role in generating actionable insights that help individuals perform more effectively in their roles. (source)
101. While 74% of organizations integrate assessments into critical stages such as hiring, onboarding, and workforce planning, a little over one-fourth do not link assessments to these essential processes. (source)
102. About 73% of organizations leverage assessment data to support decision-making and gain workforce insights. However, more than a quarter are not fully capitalizing on these tools, underscoring the importance of stronger data integration to maximize results. (source)
103. Nearly 85% of businesses use HR and talent management software, and 70% of leaders plan to increase investment in this technology. (source)
104. About 54% of companies have implemented a Talent Management Programme (TMP). 46% of employers do not have a TMP. (source)
105. Regarding long-term planning related to their staff as key business, among those with a TMP, 34% are focusing on development opportunities for their staff more than a year ahead, and an additional 25% are planning over two years in advance. (source)
106. Apart from formal TMPs, 94% of companies provide training to their staff, with only 6% not offering any training. Of those without training outside a TMP, 3% have a formal strategy elsewhere. (source)
107. The primary reason for having a TMP, cited by 83% of companies with one, is to retain existing staff, believing it crucial to prevent losing top talent. (source)
108. Companies with a TMP are 18% less likely to lose junior managers. (source)
109. Beyond retention, 79% of organizations with a TMP emphasize developing their people as a core organizational value. Their strategies include offering career progression opportunities, structured support for career growth, and linking performance to clear objectives and culture. (source)
110. The third most common reason (72%) for implementing a TMP is to foster business growth by developing new leaders. (source)
111. The private and non-profit sectors are most likely to anticipate increases in recruitment and talent management budgets compared to the public sector. (source)
112. Only 63% of organizations gather data for staffing decisions, but only a minority use a thorough approach. Specifically, 21% collect data for predicting hiring needs, 16% for evaluating talent availability, and 28% for pinpointing retention problems internally. (source)
113. According to a survey, companies that found their talent management highly effective were significantly more likely to outperform competitors compared to others. (source)
Conclusion
As the talent management statistics show, attracting, developing, and retaining top talent is challenging.
With the workforce rapidly evolving, skills gaps widening, and competition for the best employees fiercer than ever, effective talent management is critical for companies that want to succeed.

Other Related Statistic Articles You Should Know:
- 30+ Powerful Team Building Statistics to Boost Workplace Performance
- 87+ Training Industry Statistics & Trends for HR and L&D Professionals
- Global IT Outsourcing Statistics: Key Trends and Insights
- 90+ Interesting Marketing Jobs Statistics & Facts (Latest Report)
- 80+ Employee Benefit Statistics: Insights and Trends
- The Most Important Wealth Management Statistics You Can’t Afford to Ignore
- Enterprise Data Management: Essential Statistics and Emerging Trends
- Top Reputation Management Statistics and Trends to Improve Your Brand
- 36 Helpful Social Worker Burnout Statistics To Know
- 100 Business Process Outsourcing Statistics & Facts
- Top HR Outsourcing Statistics and Trends Every Business Must Know
- The Top Outsourcing Statistics You Shouldn’t Ignore
- 47+ Shocking 4-day Work Week Statistics To Know
- 105+ Supply Chain Statistics & Facts You Can’t Ignore
- 50+ Interesting Employer Branding Statistics And Trends
- Job Seekers Statistics: Unemployment Rates, Preferences, Challenges
- 95 Interesting Job Interview Statistics and Huge Trends To Know
- 60+ Helpful Change Management Statistics & Facts
- 65+ Employee Performance Management Statistics & Trends
- Workforce Management Statistics: Trends, Insights, & Opportunities
- 73 Revealing Workplace Distraction Statistics
- Workplace Romance Statistics: How Common Is Workplace Romance?
- 40+ Top Workplace Conflict Statistics You Should Know
- The State of Workplace Communication: Key Statistics and Trends
- 55 Workplace Collaboration & Teamwork Statistics