
Are you ready to unlock the secrets of the supply chain industry?
As a professional in this field, you know how crucial it is to stay ahead of the curve regarding the latest trends and statistics. And that’s exactly what this article promises to deliver.
Get ready to dive into the most up-to-date and insightful supply chain statistics, carefully curated to give you a competitive edge in the market.
From the rise of digital twins to the growing importance of sustainability, we’ll explore the trends shaping the future of supply chain management.
Whether you’re new to the industry or an expert, this article will provide the knowledge and insights you need to stay ahead of the game.
So, buckle up and join us on this journey into the world of supply chain statistics – your business’s future depends on it!
Key Supply Chain Statistics (Editor’s Top Picks)
- The global supply chain management market size was $25.74 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach around $72.1 billion by 2032.
- Enhancing visibility in manufacturing and supply chains (55%) is the main business priority for most leaders overall, but this is no longer true for smaller organizations.
- 73% of supply chains felt pressure to enhance and expand their delivery capabilities.
- Artificial Intelligence is projected to be worth about $17.5 billion in the global supply chain management software market by 2028.
- Artificial Intelligence-enabled supply chains are 67% more effective than non-AI counterparts due to reduced risks and lower overall costs.
- The Digital Supply Chain Market was valued at $5.4 billion in 2023 and is predicted to reach $12.8 billion by 2030.
- Supply chain disruptions mainly drive up costs, impacting 84.6% of businesses.
- 24.7% of supply chain professionals consider delivery costs the biggest challenge for B2C e-commerce companies.
- Almost half of companies (48%) are feeling the pressure to make their supply chains more sustainable.
- Technological advancements are being embraced by 78% of companies to enhance operational efficiency in product development.
- 37% of supply chain retailers are promoting a corporate culture of shared information, seen as necessary to build flexibility into supply chains.
- The Supply Chain Management Software market is expected to reach $20.13 billion in 2024 and grow at a CAGR of 4.13% to reach $24.65 billion by 2029.
- The USA, UK, France, Germany, and Canada are the top countries for studying supply chain management.
General Supply Chain Statistics & Facts

1. The global supply chain management market size was $25.74 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach around $72.1 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.9% from 2023 to 2032. (source)
2. Oracle, based in the United States, reported revenue streams of approximately $1.7 billion in the supply chain management software sector in 2020. (source)
3. Enhancing visibility in manufacturing and supply chains (55%) is the main business priority for most leaders, but this is no longer true for smaller organizations. (source)
4. North America had the largest supply chain market share in 2022. (source)
5. The Global AI in Logistics and Supply Chain Market Ecosystem was valued at $1.7 billion in 2018 and is projected to reach $12 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 24%. (source)
6. A reduction in supply chain costs from 9% to 4% (or from 12% to 7%) can double net profits if the net profit on sales is 5%. (source)
7. Responding to customer demands for faster, more accurate, and unique fulfilment is a top priority for 30% of supply chain leaders. (source)
8. Nearly 63% of companies do not use any technology to monitor their supply chain performance. (source)
9. Analytics are deemed important for reducing landed costs by 81% of supply chain professionals. (source)
10. In 2020, 50% of manufacturing supply chains were expected to be capable of direct-to-consumer shipments and home delivery. (source)
11. 70% of supply chain officers believed the supply chain would be a key driver of improved customer service by 2020. (source)
12. 73% of supply chains felt pressure to enhance and expand their delivery capabilities. (source)
13. Businesses with optimized supply chains have 15% lower costs, less than 50% of inventory holdings, and three times faster cash-to-cash cycles. (source)
14. In a 2021 survey, 40% of supply chain professionals indicated they had integrated cloud computing and storage technologies into their operations. (source)
15. Inventory and network optimization tools are expected to have the highest adoption rates in the next five years. (source)
16. Artificial Intelligence is projected to be worth about $17.5 billion in the global supply chain management software market by 2028. (source)
17. Artificial Intelligence-enabled supply chains are 67% more effective than non-AI counterparts due to reduced risks and lower overall costs. (source)
18. Almost half of businesses in a survey stated they were enhancing their manufacturing capacity, collaboration with supply chain partners, or supply chain speed. (source)
19. The global supply chain pressure index dropped to -0.85 points in April 2024, down from -0.3 points the previous month. After the COVID-19 pandemic, the supply chain pressure index has returned to pre-pandemic levels. (source)
20. The Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 17.31% over the forecast period. (source)
21. During the COVID-19 pandemic, 12% of retailers reported severe supply chain disruptions. (source)
22. The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing market in the supply chain management sector. (source)
23. As of 2020, 64% of retailers worldwide had adapted their supply chains for e-commerce due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and 28% faced shortages and out-of-stock. (source)
24. The Digital Supply Chain Market was valued at $5.4 billion in 2023 and is predicted to reach $12.8 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 13.0% from 2024-2030. (source)
25. In a survey, 73% of supply chain professionals believed big data analytics would be very important to their supply chains. (source)
26. The global supply chain management software market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 3.8% from 2023 to 2028. The market is projected to reach over 16 billion U.S. dollars by 2028. (source)
27. In 2022, demand planning led the supply chain management software market with a 35% market share. (source)
28. The average base salary for a Supply Chain Manager ranges from $111,054 to $142,315, with an average of $125,640. (source)
29. The supply chain analytics market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 19.28% from 2023 to 2028. It is also expected to increase by $10.38 billion. (source)
30. The cloud-based segment was the largest in the supply chain analytics market, valued at $2.47 million in 2018. (source)
31. North America is expected to contribute 38% to the global supply chain analytics market growth during the forecast period. (source)
32. 23% of supply chain respondents plan to invest in 3D printing. (source)
33. In a 2019 survey, 40% of supply chain leaders planned to invest in blockchain technologies. Also, 34% of respondents planned to invest in AR and/or VR.(source)
34. 46% of supply chain leaders plan to invest in sensors and IoT. (source)
Supply Chain Challenges Statistics
35. Supply chain disruptions mainly drive up costs, impacting 84.6% of businesses. (source)
36. In 2021, over 50% of supply chain professionals found disruptions and shortages “extremely/very challenging”, with demand-side issues like faster response times being major hurdles. (source)
37. The GSCPI indicates that disruptions in 2021 and 2022 were three to four standard deviations above the historical average. (source)
38. Supply chain pressures increased headline, food, and tradable core inflation by approximately 2 percentage points during the 2020–22 period. (source)
39. Workforce shortages affect 76% of supply chains, with 37% reporting significant deficits, especially in transportation and warehousing roles. (source)
40. Supply chain pressure shocks positively contributed to inflation throughout the post-2020 period. (source)
41. 24.7% of supply chain professionals consider delivery costs the biggest challenge for B2C e-commerce companies. (source)
42. 57% of businesses have limited visibility across their supply chains. (source)
43. Global supply chain pressures peaked at almost 4.5 standard deviations in late 2022 during the pandemic. (source)
44. Almost half of companies (48%) are feeling the pressure to make their supply chains more sustainable. (source)
45. Supply chain pressures eased in the first half of 2021 but gradually increased from July 2021, reaching an all-time high in June 2022. (source)
46. About 42% of automotive and assembly industry business leaders considered demand variability the most critical factor, making their businesses vulnerable to supply chain disruptions. (source)
47. A 2020 study found that global value chains in the communication equipment sector had the highest overall shock exposure. (source)
48. 37% of global consumers reported switching to online shopping due to supply chain issues. (source)
49. Six out of ten online shoppers in Indonesia reported changing their shopping habits due to supply chain problems. (source)
50. During a survey, demand-side challenges, such as faster response times, were cited among the most difficult hurdles for supply chain companies. (source)
51. Supply chain disruptions cause significant economic hardship, costing organizations worldwide an average of $184 million annually, according to a 2021 survey. (source)
52. Regionally, the financial burden is highest in the United States, where respondents’ organizations faced an estimated average annual cost of $228 million. (source)
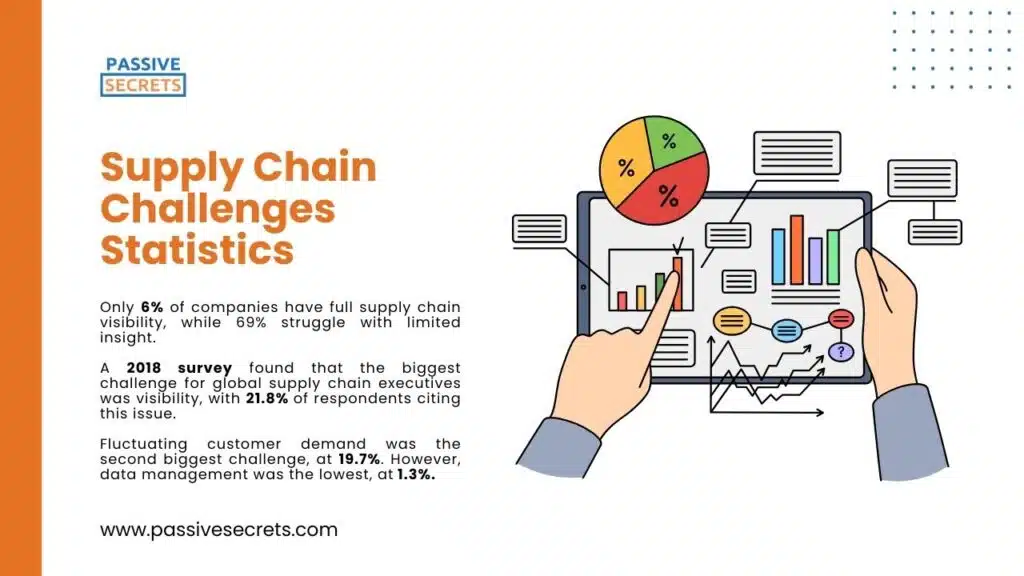
53. Only 6% of companies have full supply chain visibility, while 69% struggle with limited insight. (source)
54. A 2018 survey found that the biggest challenge for global supply chain executives was visibility, with 21.8% of respondents citing this issue. (source)
55. Fluctuating customer demand was the second biggest challenge, at 19.7%. However, data management was the lowest, at 1.3%. (source)
Supply Chain Innovation Statistics
56. The first-ever Pan-African landscape assessment revealed 350 innovators digitizing African health supply chains. (source)
57. Innovators are based in 27 African countries, with a concentration in Nigeria, South Africa, Kenya, and Egypt. (source)
58. 25% of innovators work in more than one category. (source)
59. Nearly 50 partnerships have been formed to provide governments with technology-enabled supply chain solutions. (source)
60. 80% of leaders surveyed by PWC say their supply chain tech projects have not delivered the expected returns. (source)
61. Technological advancements are being embraced by 78% of companies to enhance operational efficiency in product development, paving the way for more practical and economical production of smaller product batches. (source)
Supply Chain Distribution Statistics
62. In 2021, North America had the highest share of disruptive events at 47%. Also, 11,642 reported supply chain disruptions worldwide were reported. (source)
63. Companies with an extensive supply chain distribution plan take only two days for order fulfilment. (source)
64. Companies without a supply chain distribution plan can take up to 10 days for order fulfilment. (source)
Retail Supply Chain Statistics
65. Measures imposed during the COVID-19 pandemic affected the retail supply, leading to higher rates of out-of-stock and overstocked consumer goods. (source)
66. In 2020, the global inventory distortion related to out-of-stock grocery products was valued at $568.7 billion. (source)
67. In 2020, the imbalance between supply and consumer demand resulted in an out-of-stock value of $176.7 billion. (source)
68. While retailers struggled with inventory distortion costs at the store level, manufacturers faced even higher costs due to disrupted demand. (source)
69. Inventory distortion caused a loss of $580 million for stores for supply chain retailers. (source)
70. The imbalance between supply and demand during the pandemic resulted in costs amounting to $677 million at the manufacturing level. (source)
71. More than 82% of retailers surveyed by The Economist Intelligence Unit reported significant disruption to their supply chains due to COVID-19. (source)
72. In the US, 94% of retailers reported significant disruption, compared to 75% in Europe and 78% in Asia Pacific. (source)
73. Over the past three years, 40% of supply chain retailers focused on introducing new technology to increase supply chain resilience. (source)
74. 37% of supply chain retailers are promoting a corporate culture of shared information, seen as necessary to build flexibility into supply chains (source)
75. In the past three years, 45% of supply chain retailers developed an end-to-end information flow. (source)
76. 39% of supply chain retailers focus on collaboration and information-sharing between departments. (source)
77. Two in five (39%) have developed deep, long-term relationships with suppliers and customers to enhance resilience. (source)
78. Nearly one-third (32%) of supply chain retailers regularly reassess supplier performance to improve flexibility. (source)
79. More than half of retail (58%) and consumer products (55%) executives are focused on building agility to adapt faster to changes in demand. (source)
80. 33% of respondents from a global survey said smart connected technologies were essential for addressing potential disruptions in the retail supply chain. (source)
81. 18% of respondents considered using Big Data for demand predictions less important. (source)
82. As of 2020, around 56% of global retailers reported moderate disruption in their supply chains due to the COVID-19 pandemic. (source)
Supply Chain Management Statistics
83. The global supply chain management market size is projected to grow from $28.6 billion in 2023 to $81.9 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 11.1% from 2024 to 2033. (source)
84. The U.S. supply chain management market is expected to grow from $7.89 billion in 2023 to $23.84 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 11.7%. (source)
85. North America had the largest share of 39.34% in 2023 in the global supply chain management market. (source)
86. The Supply Chain Management Software market is expected to reach $20.13 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.13% to reach $24.65 billion by 2029. (source)
87. The top countries for studying supply chain management are the USA, UK, France, Germany, and Canada. (source)
88. Over 170 accredited universities in the USA offer Master’s programs in Supply Chain Management, covering logistics, risk management, operations management, procurement, sustainability, and technology integration. (source)
89. The annual cost of studying Supply Chain Management in the USA typically ranges from $50,000 to $80,000. (source)
90. In the UK, the cost for international students to pursue an SCM program ranges from £17,090 to £32,300 per year. (source)
91. In Canada, studying supply chain management costs between 30,000 and 140,000 CAD per year. (source)
92. Canada offers the Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP) program, allowing international students to gain valuable work experience after their studies. (source)
93. Revenue in the Supply Chain Management Software market in the United Kingdom is expected to reach $1.05 billion in 2024. (source)
94. The SCM software market in the UK is forecasted to grow at an annual rate (CAGR 2024-2028) of 5.89%, reaching a market volume of $1.32 billion by 2028. (source)
95. The average spend per employee in the UK Supply Chain Management Software market is projected to reach $29.67 in 2024. (source)
96. In 2020, Germany’s SAP maintained its leading position in the supply chain management software market, with approximately $4.4 billion in revenue. (source)
97. The cost of studying supply chain management in Germany is around €20,000 per year. (source)
98. Australia’s Supply Chain Management Software market will reach $335.5 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4% to $408.2 million by 2029, with an average spend per employee expected to be $22.94 in 2024. (source)
99. China’s Supply Chain Management Software market will reach $0.79 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.08% to $1.22 billion by 2029, with an average spend per employee expected to be $1.01 in 2024. (source)
100. The Global Retail Supply Chain Management market was valued at $31.11 billion and is expected to grow to $58.87 billion by 2030. The market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9.54% from 2024 to 2030. (source)
101. The cloud-based deployment phase of the retail supply chain management market is expected to experience high demand, with a CAGR of 14.2% over the coming years. (source)
102. The U.S. is predicted to account for over 79% of the North American supply chain management market share by 2030. (source)
103. Revenue in Nigeria’s Supply Chain Management Software market is expected to reach $31.18 million in 2024. (source)
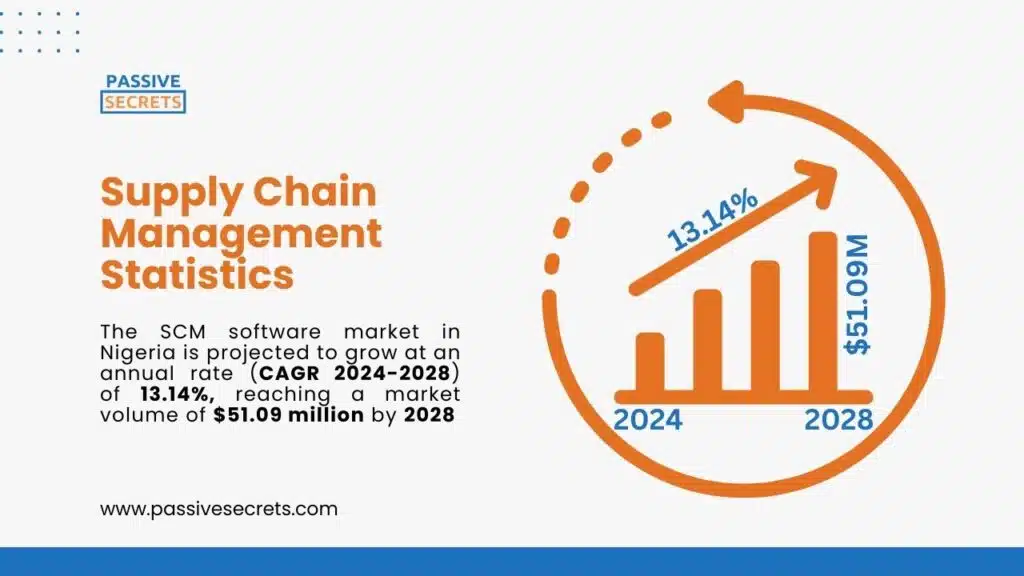
104. The SCM software market in Nigeria is projected to grow at an annual rate (CAGR 2024-2028) of 13.14%, reaching a market volume of $51.09 million by 2028. (source)
105. The average spend per employee in Nigeria’s Supply Chain Management Software market is projected to be $0.46 in 2024. (source)
106. In global comparison, the most revenue will be generated in the United States, amounting to $10,230 million in 2024. (source)
Supply Chain Trends
1. ArtificialIntelligence in Operations
Artificial intelligence (AI) advances are occurring at an unprecedented rate and offering numerous immediate returns, particularly in intelligent sourcing, inventory management, and logistical route planning.
Cobots drive warehousing efficiency through picking and packing, loading and unloading, and moving heavy objects; computer vision supports defect detection and object recognition; robotics enable safer assembly and welding; and augmented reality advances training, maintenance, and quality control.
Meanwhile, machine learning (ML), a subset of AI that allows computers to learn without being explicitly programmed, will be used to make predictions and decisions about demand forecasting, quality control, new product development, and much more.
Through 2024, 50% of supply chain organizations will invest in applications that support artificial intelligence and advanced analytics capabilities.
2. Investment in Systems and People
As supply chain technology adoption escalates, investing in people through training and development on the latest technology will continue to create a culture of innovation and encourage employees to share ideas that lead to supply chain success.
3 Transparency and Visibility Beyond Tier 1 and 2
Breaking the visibility barrier beyond Tier 1 allows organizations to look across their extended supply chain into partners, build greater and deeper insights into root causes, identify new risks that occur further into the supply chain, and drive ESG goals through better traceability and transparency.
Technology tools such as control towers and digital twins can surface critical sub-tier supplier relationships, highlight common sub-tier suppliers and factory locations, and provide clear insight into the depth of an organization’s supply chain.
Less than half (43%) of organizations have limited to no visibility of tier-one supplier performance.
4. Low-code Platforms
Most supply chain tasks can be fully or partly automated through low-code platforms, which use a wide range of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and pre-packaged integrations to link previously separate systems.
These cut development time, enabling companies to swiftly react and adapt their applications to new market conditions, disruptive events, or changing strategies. They also enable business users with little technical knowledge to quickly build, test, and implement new capabilities.
More than two-thirds of enterprises have already adopted low-code to their supply chains.
5. Electric Vehicles, Transport, and Logistics
The logistics sector is also undergoing rapid transformation. The adoption of warehouse and port automation will expand as organizations commit to emissions reduction targets and battery technology evolves to extend distance limits for electric trucks, buses, and delivery vehicles.
Conclusion
The supply chain has become a fundamental component of success in today’s ever-changing corporate environment.
The figures we’ve examined present a clear picture: the supply chain is a complicated, dynamic system that necessitates meticulous planning, collaboration, and optimization.
To remain competitive, firms must embrace data-driven decision-making and implement new solutions.
Understanding and acting on supply chain statistics can help businesses position themselves for long-term success and better serve their customers in an ever-changing global economy.
FAQs
What does supply chain management mean?
Supply Chain Management oversees the entire production flow of goods and services, from raw materials to delivering the final product to the consumer. It manages production planning, business forecasting, and demand planning throughout the entire business process.
What is the global supply chain size?
The global supply chain management market was valued at USD 28.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow to USD 45.2 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast period (2022-2027).
Which country experiences the highest demand for supply chain management professionals?
The United States tops the list, with a robust market demand fueled by its expansive logistics networks and diverse industrial sectors.
Which region has the largest market share in supply chain management?
North America has the largest supply chain management market share.
Who are the prominent players in the Supply Chain Management market?
Ten prominent players are in the supply chain management market: SAP (Germany), Oracle (US), Infor (US), Descartes (Canada), Manhattan Associates (US), IBM (US), Logility (US), Kinaxis (Canada), Blue Yonder (US), and Korber (US).
How does technology impact supply chain management?
Technology significantly impacts supply chain management by enhancing visibility, efficiency, and communication. Technologies like RFID, IoT, blockchain, and AI enable real-time tracking, predictive analytics, and automation, leading to better decision-making and more resilient supply chains.
Why is supply chain management important?
Supply chain management (SCM) is essential for companies as it helps streamline operations, reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction. Effective SCM can result in faster production cycles, better inventory management, and stronger relationships with suppliers and customers.
What are some common challenges in supply chain management?
Common challenges in supply chain management include demand variability, supply chain disruptions, maintaining optimal inventory levels, managing supplier relationships, and ensuring sustainability. Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning and advanced tools and technologies to mitigate risks and improve efficiency.

Other Related Statistics You Shouldn’t Miss
- 80+ Employee Benefit Statistics: Insights and Trends
- Enterprise Data Management: Essential Statistics and Emerging Trends
- 93 Talent Management Statistics to Help You
- Top Reputation Management Statistics and Trends to Improve Your Brand
- 36 Helpful Social Worker Burnout Statistics To Know
- 100 Business Process Outsourcing Statistics & Facts
- Top HR Outsourcing Statistics and Trends Every Business Must Know
- The Top Outsourcing Statistics You Shouldn’t Ignore
- 47+ Shocking 4-day Work Week Statistics To Know
- 50+ Interesting Employer Branding Statistics And Trends
- Job Seekers Statistics: Unemployment Rates, Preferences, Challenges
- 95 Interesting Job Interview Statistics and Huge Trends To Know
- 60+ Helpful Change Management Statistics & Facts
- 65+ Employee Performance Management Statistics & Trends
- Workforce Management Statistics: Trends, Insights, & Opportunities
- 73 Revealing Workplace Distraction Statistics
- Workplace Romance Statistics: How Common Is Workplace Romance?
- 40+ Top Workplace Conflict Statistics You Should Know
- The State of Workplace Communication: Key Statistics and Trends

